Article:- Biotechnology and it’s Applications-DNA Fingerprinting (Class-12)Zoology
DNA Fingerprinting (Reference:-National Human Genome Research Institute, Government of India)
Definition:- DNA fingerprinting is a technique that shows the genetic makeup of living things. It is a method of finding the difference between the satellite DNA regions in the genome.
What is DNA Fingerprinting:-
Satellite DNA regions are stretches of repetitive DNA which do not code for any specific protein. These non-coding sequences form a major chunk of the DNA profile of humans. They depict a high level of polymorphism and are the basis of DNA fingerprinting. These genes show a high level of polymorphism in all kind of tissues as a result of which they prove to be very useful in forensic studies.
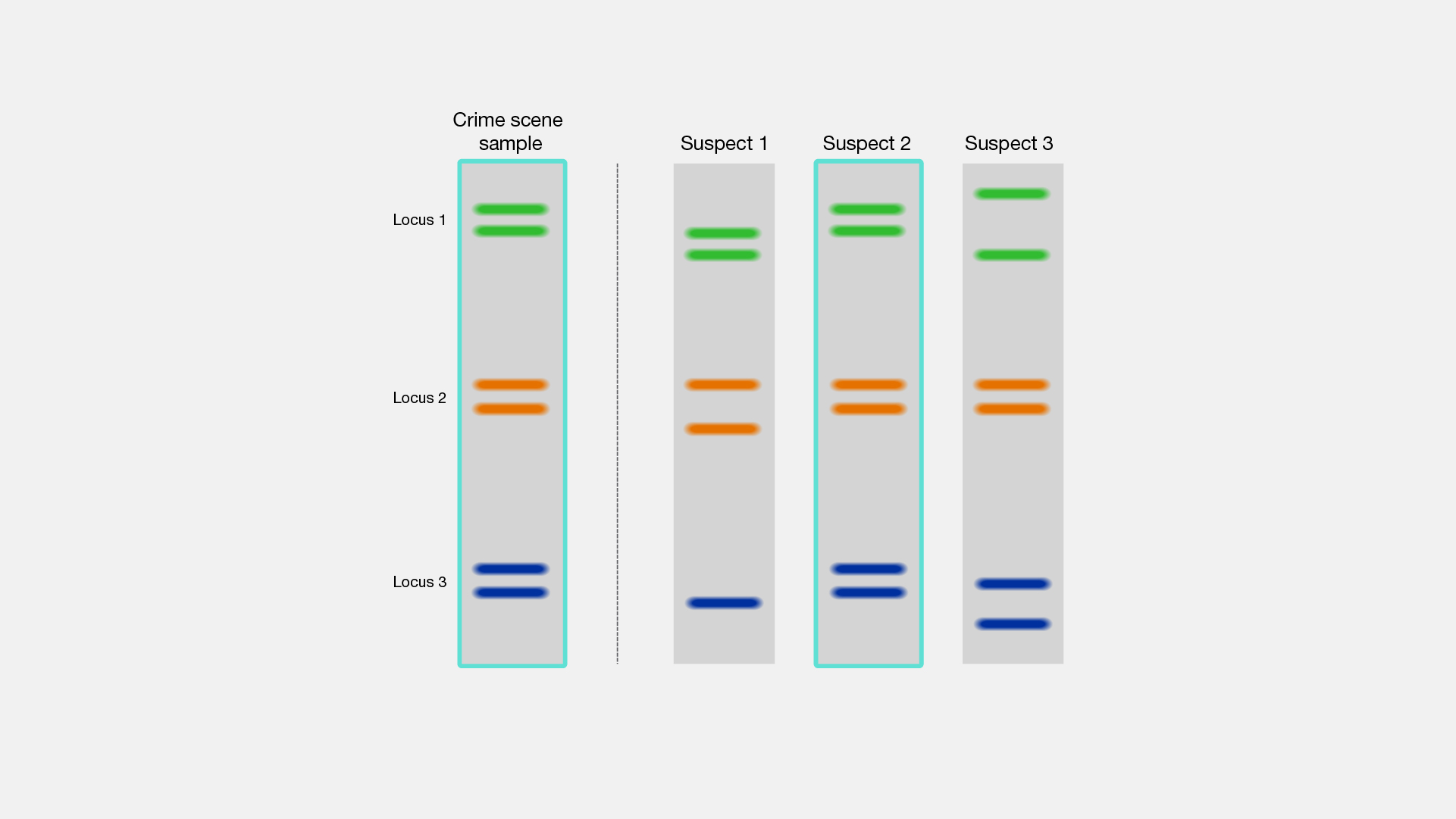
Any piece of DNA sample found at a crime scene can be analysed for the level of polymorphism in the non-coding repetitive sequences. After the DNA profile is traced, it becomes easier to find the criminal by performing the DNA fingerprinting for the suspects.
Apart from crime scenes, Fingerprinting applications also prove useful in finding the parents of an unclaimed baby by conducting a paternity test on a DNA sample from the baby.
Method & Process:-
Alec Jeffreys developed this technique in which he used satellite DNAs also called VNTRs (Variable Number of Tandem Repeats) as a probe because it showed the high level of polymorphism.
=>☞ Following are the steps involved in DNA fingerprinting:-
1. Isolating the DNA.
↓
2. Digesting the DNA with the help of restriction endonuclease enzymes.
↓
3. Separating the digested fragments as per the fragment size by the process of electrophoresis.
↓
4. Blotting the separated fragments onto synthetic membranes like nylon.
↓
5. Hybridising the fragments using labelled VNTR probes.
↓
6. Analysing the hybrid fragments using autoradiography.

Figure – DNA Fingerprinting Steps
Applications of DNA Fingerprinting:-
As discussed earlier the technique of fingerprinting is used for DNA analysis in forensic tests and paternity tests. Apart from these two fields, it is also used in determining the frequency of a particular gene in a population which gives rise to diversity. In case of the change in gene frequency or Genetic Drift, Fingerprinting can be used to trace the role of this change in evolution.
Important MCQ Type Questions:-
MCQ.1): ______________Is the method to identify a particular individual rather than simply identifying a species or trait.
a) RNA fingertesting
b) DNA fingerprinting
c) Colour printing
d) UV identifier
MCQ.2): The DNA fingerprinting method is used by scientists to distinguish between individuals and they only use ______________ Sample.
a) Cytoplasm
b) Cell
c) DNA
d) Ribosomal
MCQ. 3): The DNA fingerprinting process or technique was invented by _________________ In 1985.
a) Alexa Brown
b) Bill Jonas
c) Neon Mask
d) Alex Jeffreys
MCQ.4): Which of the following can be biological samples for DNA fingerprinting?
a) Blood
b) Hair
c) Saliva
d) All of them
MCQ.5): When DNA is recovered from cells or tissues then this step in DNA fingerprinting is___________________________.
a) Isolation of DNA
b) Collection of DNA
c) Centrifugation of DNA
d) Formation of DNA
MCQ.6): Which of the following enzyme is useful to cut DNA into fragments?
a) Scissor
b) Senssor
c) Restriction
d) Freedom
MCQ.7): _______________is the process by which DNA fragments get separated on the basis of size.
a) Electropoetic
b) Gel electrophoresis
c) Gel purification
d) None of these
MCQ.8): The DNA is _________________ charged.
a) Positively
b) Gamma
c) Sigma
d) Negatively
MCQ.9): The process where DNA fragments are transferred to nylon sheet on the gel for soaking is called as ______________________.
a) Southern blotting
b) Blood clotting
c) Northern blotting
d) Nitro Blot
MCQ.10): Which technique involves alignment of hybridized membrane with X-ray film?
a) Radiology
b) Neurotechnology
c) Autobiography
d) Autoradiography
Answers:-
1). b) DNA fingerprinting
2). c) DNA
3). d) Alex Jeffreys
4). d) All of them
5). a) Isolation of DNA
6). c) Restriction
7). b) Gel electrophoresis
8). d) Negatively
9). a) Southern blotting
10). d) Autoradiography.